What is printing in textile
Printing word derived from the Latin word meaning “pressing and indirect pressure application”. Textile printing is applying color to fabric in definite designs and patterns. A technique decorating fabric with pigments, dyes, or other materials in which fabric is pretreated or after dying. It is a branch of wet textile processing in which fabric is printed to produce different attractive textile printing designs and patterns. Usually, printing is done on one side of the fabric. There are different types of printing in textile techniques chemicals and dyestuff used on fabric.
Textile printing is related to dyeing, however, the dying fabric is uniformly in one color. Also, in these types of printing on clothes, one or more colors are used to fabricate a specific design and pattern. These dyes or pigments are applied discontinuously or locally. In this article the types of printing methods in terms of machinery used to deliver print past and also, the mode by which paste is delivered on a substrate. It may be flat or rotary screen printing types copper roller inkjet or any other mechanism.
There is a printing carried out in the Indian subcontinent during the 4th century BCE. Moreover, block printing types date back to about 300 CE in Egypt. The origin of textile printing started with woodblock printing, the oldest technique used.
Different types of printing techniques on fabric
Fabric printing refers to producing beautiful patterns and designs on textile substrates. Here is a list most popular methods of printing used to do this.

The most beautiful swirls of textile printing design and patterns on a pretty fabric you bought from a fabric store look effortless. But this fabric printing is all anything. It is challenging to achieve perfection and precision in detail with durable color on the fabric surface. In the production of textile processing, patterns, and designs are often printed in the final stage. When you read about it, the printing process is sample enough – pigments or dyes are consumed to make these designs and patterns. But to make stick there, separately without a tangle, yard after yard – that is the more crafty part.
The different types of printing on fabric are roller printing, heat transfer printing, block printing, photo printing types, rotary printing, discharge printing, pigment printing, 3D printing types, direct-to-garment (DTG) printing, transfer printing, reactive printing, and resist printing.
If you are looking for ways to do T-shirt printing, which is a subject itself, check out the post on T-shirt printing.
4 Basic textile printing methods
The four most important types of printing on fabric or common style are
- Direct printing
- Transfer printing
- Discharge printing
- Resist-printing
Read more on common styles of textile printing here. Read more on common styles of textile printing
Textile fabric printing – 8 popular methods
- Block Printing
- Roller Printing
- Screen Printing
- Transfer Printing
- Ink-jet printing/ Digital textile printing
- Jet spray printing
- Resist Printing
- Pigment Printing
Roller printing
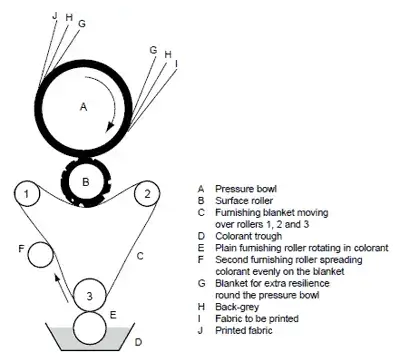
Roller printing is most widely used in early textile printing methods. This technique is used whenever fabric is to be printed same design in the long run. However, the modern machine consists of one of the cast iron large cylinders which possess a textile printing design. A thick blanket is used as a support for fabric, called backing fabric. This backing fabric is a gray side of fabric, blanket provides support to undue printing. It may be cotton fabric, but nowadays a continuous belt of Nylon. This belt is appropriately tensioned, so the fabric moved in the machine as flat on cylinders.
The pattern is engraved on copper rollers. So, high-quality engraving and cleaning are required for good-quality printing. Since, types of printing on cloth roller are provided with a rotating color past, immersed partially into the printing paste. Also, a doctor blade is used to remove the excess past from unengraved areas from these rollers.
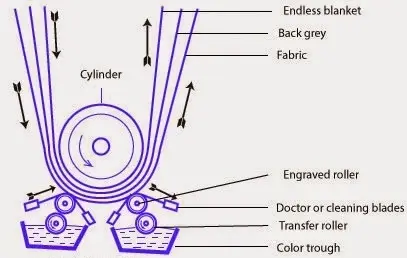
The printed fabric passes from the main cylinder to the drying and steaming chambers to fix the color. This machine has only one side of the fabric. The relatively new machine the Duplex roller, it is a combination of two rollers, which can print both sides of the fabric. Also, modern textile printing machines are more smooth-running precision machines fitted with carefully designed roller bearings and hydraulic or pneumatic mechanisms to ensure uniform pressure and more flexibility. Pressure is controlled from the control panel, and each roller roller controlled individually. Now electromagnetism and electric servo motors provide smooth running, variable speed drives. Washing of backing and roller is done automatically.
Advantages of roller printing
- Design capability is high
- Fine marking
- Multiple tones or colors
- High production
Disadvantages of roller printing
- Copper cylinders are expensive ones
- Long production run feasible
- Need many skilled workers
Block Printing
Block printing was first developed in China. The earliest known example of block printing actually dates back to the Diamond Sutra from 868 A.D (British Museum currently), and probably may also be two thousand years old. Wooden blocks carved with a design are made of solid pieces of wood or bonded closely with grained wood. However, fine lines are usually built with copper strips. When construction on a large area several blocks joined and the space was filled with wool felt.
The color past is applied in a controlled manner and achieved by a ‘sieve’. A small tub filled with starch past and waterproof fabric stretched on a frame. Also, a woolen fabric relatively small piece is used as a sieve. So, the sieve is saturated with dye color paste and placed on a waterproof fabric. For each impression, a boy called ‘tiered’ spread the paste on a woolen sieve with a large brush. The printer charged the block by pressing it against the wool. The block is then carefully positioned on the fabric and the pitch pin is positioned as a guide. After printing a table length of one block followed by a second and so on, the stretched frame is completed.
This fabric table was then allowed to dry and started the second table. If using more than one color other colors are applied one by one to complete the design. However block printing becoming laborious and costly for use commercially, while one of the most common types of textile printing design can be made in this way.
Advantages of block printing
- Simple and cost-effective
- A more versatile large number of surfaces, fabric, paper
- Artistic and handmade
- eco-friendly and sustainable for textile
Disadvantages of block printing
- The process of carved design is a time-consuming
- Limited color option
- Achieving consistent prints can be challenging
- Very low in production
- Block printing requires skill in carving and printing
Screen printing

Screen printing types can be categorized into three ways
- Flat screen printing – mostly used different types of printing on fabric as ready-made objects (t-shirts, bags)
- Rotary screen printing – this printing is used on the entire fabric roll, as the initial cost is high because of the preparation of the cylinder, and repetition costs are very high.
- Hand-screen printing – it was introduced to the studio by Andy Warhol, it has been a quickly accepted technique that is accepted by individual artists also, usually screen prints their production using homemade methods.

Advantages of screen printing
- Fast process
- Changeover of patterns is fast
- Continuous patterns
Disadvantages of screen printing
- Limited design
- Small repeats
Heat transfer printing
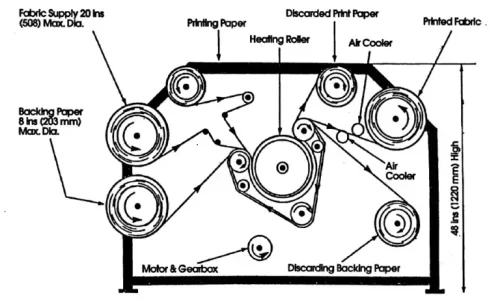
There are two methods used
- Dry heat transfer printing
- Wet heat transfer printing
In dry heat, a conventional method a cylinder eclectically heated is used to press a fabric and paper against heat heat-resistant blanket. Also, in wet heat transfer printing method uses infrared heat vacuum transfer types of printing in textiles, the fabric and printed paper are passed between infrared heaters and a cylinder which is perforated and protected from excess heat by the shield. So, wet heat transfer printing uses heat in a wet atmosphere which vaporizes the dye pattern on the fabric. The process of transfer print into substrate ink is in close contact with a substrate, and this is later on transferred permanently to said substrate by heat and pressure. When said ink is applied by using a computerized method inputting an image of the desired pattern, this ink is transferred on a tuner, and the desired image and character are transferred onto paper said temporary transfer support.

Advantages of heat transfer printing
- Easy handling of units
- Low-cost operation
- Flexible training of operators
- Better marking and clarity
- A large number of designs stored
- Eco-friendly
Disadvantages of heat transfer printing
- Low production
- Mainly used for polyester, a limited use
Digital printing
If you are looking for ways to digital textile printing, which is a subject itself, check out the post on “A comprehensive digital textile printing overview“

Digital ink-jet printing is the most common way and modern printing styles on textile fabric. This digital printing can be done on any commercially available fabric. Also, in this method of printing, patterns are directly printed on fabric using a computer with an Inkjet printer, without making screen printing techniques and or rotary rollers. Since textile printing designs are prepared on a computer using design software, lead time is minimal. So, in digital printing complex designs of photographic quality can be prompt. However, as compared the productivity of ink-jet printing with rotary screen printing is very low. This is used for very short article production runs or for printing banners or flags, etc.