Resin is a viscose material that is derived from various plants and synthetically produced from chemicals. It is widely used in manufacturing, construction, art and medicine.
Resine is of two types, natural and synthetic. Natural resin is extracted from plants through a technique called tapping,( a cut in the bark). Synthetic resin is designed to be processed chemically to meet specific performance according to requirements. In this article, we discussed synthetic resin its types, and how to make it.
What is resin made of
Resin made of non-crystalline viscose polymer material composed of chemical bonding. This is the first ingredient of the plastic material before the addition of other ingredients like stabilizers, filler, pigments, catalysts, and lubricants, and before fabrication to finishing articles.
First of all to make resin, we prepare the polymer and this polymer we add
- Stabilizer
- Filler
- Pigment
- Catalyst
- Lubricant
These are known as curing agents. Thus the resin is actually the first material that is prepared from a polymer.
Types of Synthetic Resins
There are two types of synthetic resins, thermoplastic resins, and thermosetting resins. Thermoplastic-type resins can be changed into other forms under the action of heat and pressure. Thermosetting-type resins are those that after the formation can not be changed into other forms under the action of heat and pressure
- Thermoplastic resin
- Thermosetting resin
What is a Thermoplastic Resin?
Thermoplastic resins are those which can be changed into other forms under the action of heat and pressure, the process is reversible. They have secondary bonds between molecules and are loosely crosslinked. For example, polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyvinyl chloride (PVC)are examples of thermoplastic resins.
What is a Thermosetting Resin?
Thermosetting resins are those that after the formation can not be changed into other forms under the action of heat and pressure. These changes are irreversible. They have primary bonds between molecules and are strongly crosslinked. e.g.
- Phenol formaldehyde resins
- Urea-formaldehyde resins
- Melamine resins
- Acrylic resins
- Polyester resins
What is Phenol formaldehyde Resin?
Phenol formaldehyde resin is a compound when formaldehyde and phenol react together is called phenolic resin. It is available in the commercial name formatin, which contains 30~35 % formaldehyde and the rest is water. Para-formaldehyde is the evaporation of formalin which contains 90% formaldehyde and 10% rest is water.
Phenol formaldehyde resin is called phenolic resin. This material resists high temperatures and heat is involved, and with high insulating properties, is called formaldehyde resin material.
How to Prepare Phenolic Resin?
Phenolic resins are prepared by crosslinking of phenol formaldehyde with thermal-induced action. This thermal curing derives water as a by-product. On further condensation, we get bakelite resin.
To prepare phenolic resins first formaldehyde resins and then the final compound is obtained by a different method. The following reaction takes place during the formation of formaldehyde resins.
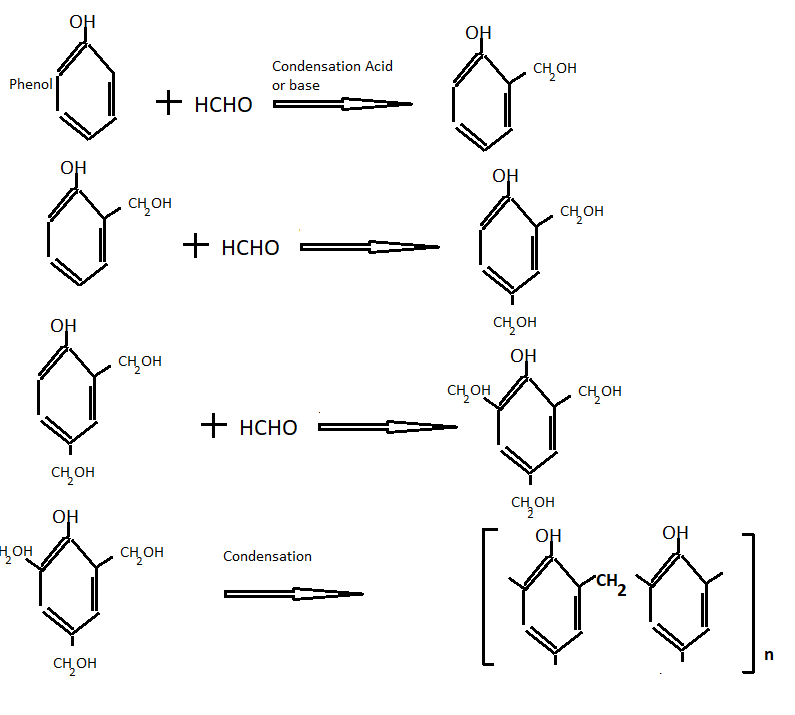
-CH2– is also called methylene bridge
On further condensation we get bakelite
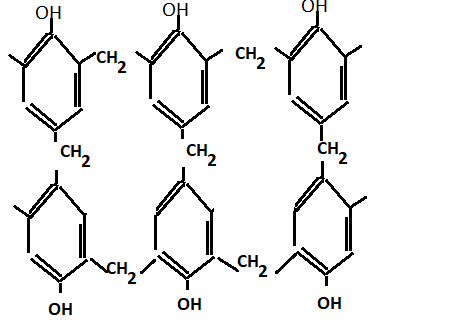
Further methylene bridges are ground into small pieces to obtain the molding powder and then the following material is added
- Resins 30Kg (molding powder)
- Filler 40~45 kg(usually wood flour)
- Hexamine ( as a gardening agent)
- MgO 1~2 kg(as a catalyst) CaO can also be used
- Colouring material4~5 Kg
- Lubricating agent ( steric acid) 0.1~0.2 kg
Properties of Phenolic Resin
- Phenolic resins are high-temperature resistance for flame 300~350 0C.
- These have high surface hardness, electric insulating properties
- Phenolic resins are highly chemical resistant, resistant to alkalies, acids, and other chemicals
- Phenol formaldehyde resin are low-cost resin
- Fire retardant
- Low toxicity and smoke emission
- Good friction properties
Uses phenolic resins
Phenolic resins are used for making molding powder used for making plywood.
Phenolic resins are also used as foaming materials high-quality foams with remarkable properties are produced by phenolic resins. Moreover, this kind of foam is fire resistant having good thermal insulating properties. Also, phenolic resins have of wide range of applications:
- Phenolic resins applications for surface coating e.g.; metals are corroded in the presence of oxygen and water.
- phenolic resins are also used to prevent metals from corrosion.
- These are also used in the plastic and paper industries.
- It is used for preparing chip board i.e. order to improve mechanical properties and to reduce water absorption.
- Phenolic resins are used for laboratory work surface
- These are used in mass transit in rail and busses
- Used in electric and electronic industries as an insulator
Types of phenolic resins
There are two types of phenolic resins, Novolac, and Resol. Novolacs resins are phenol-formaldehyde resins in which the molar ratio of formaldehyde to phenol is less than one. It is produced by using an acidic catalyst
Resol phenolic resins are produced by alkaline catalysts. It is highly cross-linked in three dimensions and suitable for high-temperature applications. Resol-type resins are caustic resins in which filler is not used. Caustic resins may be cured slowly by heating at 70~800C for 2~8 days.
Resol resin can be cured rapidly by heating with a little acid. in this way, it takes 1~6 hours for curing. The specific gravity is 1.3, tensile strength is 3000~10000 lb/ inch2 and have bonding strength 7000~ 15000 lb/inch2.
- Novolac resins
- Resol resins
Applications of Novolac Resins
- Binding resins: Novolac resins have excellent properties of adhesive and binding strength. So, these are used for barks lemmings making sandpapers, etc.
- Coating resins: In varnishes, electrical insulation, and other protective coatings. These resins are also in the manufacture of plywood
- Ion exchange resins: Novalac resins are also used in the production of ion exchange resins. These resins are useful in softening the water for textile use.
- It is used curing agent for epoxy resins.
- Used for carbon brake.
- High-temperature resistance.
Applications of Resol Resins
The resol resin is used for gulling as paper limination and engineering wood. It is used as a molding compound and adhesive used in plywood and furnishing applications. It is high heat resistance and good tensile strength are used in every shore of oil drilling.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is called resin?
Resin is a viscose material that is derived from various plants and synthetically produced from chemicals. It is widely used in manufacturing, construction, art and medicine.
What is Phenolic Resin?
Phenol resins are compounds when formaldehyde and phenol react together. It is available in the commercial name formation, also, known as phenol formaldehyde resin.
What is Resol Resin?
Resol phenolic resins are produced by alkaline catalysts. It is highly cross-linked in three dimensions and suitable for high-temperature applications. Resol-type resins are caustic resins in which filler is not used.
What is Novalac Resin?
Novolacs resins are phenol-formaldehyde resins in which the molar ratio of formaldehyde to phenol is less than one. It is produced by using an acidic catalyst
Amino resin
Amino resins have an amino group (-NH2-) in their structure is a thermosetting polymer. It is also called aminoplasts. Amino resins are polymers of formaldehyde with either urea or melamine.
Amino plastic resins are two types; Urea-formaldehyde resins, and Melamine formaldehyde resins. Urea-formaldehyde resins: these are produced by the condensation of urea and formaldehyde Hence, urea= NH2-CO-NH2 formaldehyde HCOH.
Melamine formaldehyde resins: These are produced by the condensation product of melamine with formaldehyde.
Urea-formaldehyde resins
Urea-formaldehyde resins are carried out in two separate operations. The first operation involves the formation of low molecular weight, fusible, and soluble resins, while the second operation involves a curing reaction that leads to cross-linked products.
Types of Urea-formaldehyde resins
Urea-formaldehyde resins are of two types, produced commercially and are classified into unmodified resins, and modified resins. These are used in the preparation of molding composition adhesives.
- Unmodified resins
- Modified resins
i-Unmodified resins
These are used in the preparation of molding composition and adhesives
Preparation urea-formaldehyde resins
These resins are prepared by following reactions
A-stage
Formalin is made slightly alkaline by the addition of NaOH solution being PH value 8~8.5and then Urea is added to a molar ratio Urea: HCHO,1:2
The resulting solution is boiled and referred for 15 minutes acidified with formic acid and then further boiled for 5~20 minutes. The product is neutralized with NaOH and then evaporated under reduced pressure until a solid content (70%) is reached.
Formalin (2) + urea (1) → 70% solid mass + lubricant+ stabilizer+pigment(colour)
Ist stage
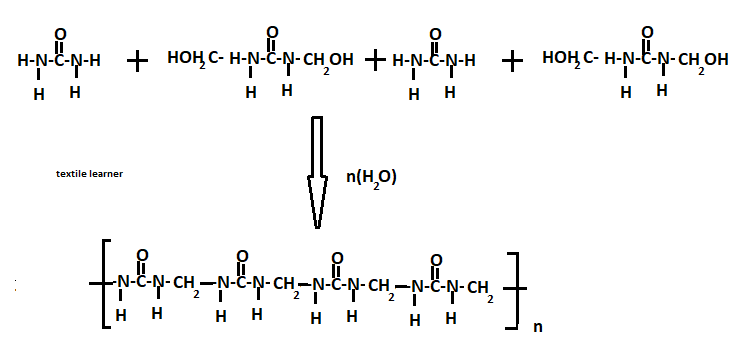
NH2-CO-NH2+ CH2O→ NH2-CO-NH-CH2-OH (methylene urea)
2nd stage
NH2-CO-NH-CH2-OH+ CH2O→ NH2-CH2-OH — CO — NH2-CH2-OH(Dimethylal urea)
A– when dimethyl-ol urea is further condensed with other molecules of urea forming a condensation polymer.
B– The linear polymer formed can condense with more formaldehyde molecules to form the cross-linked products.
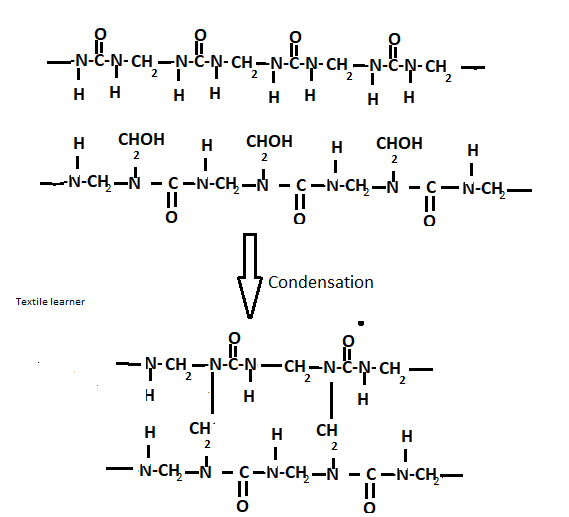
C- The dimethyl-ol urea molecules can condensate with each other to form linear polymers
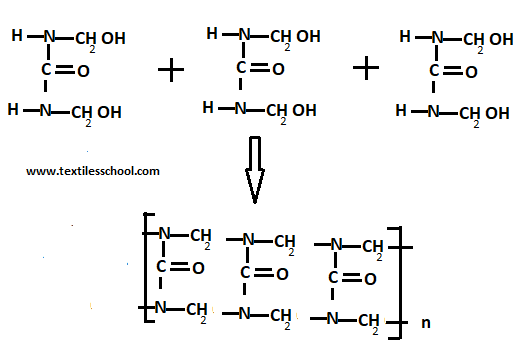
This gives rise to a complex mixture of linear and crosslinked condensation polymers known as urea-formaldehyde resins depending upon reaction conditions and resins of the different types obtained.
ii-Modified resins
Unmodified resins are not suitable for use in the surface coating because they are invaluable in common solvents ( alcohol ether etc) and do not interact readily with other resins. These limitations are overcome when the resins are modified.
Normally alcohol (normal butane) is mostly used for this purpose. The PH value is adjusted to 8 and urea is added to a given molar ratio
Urea: HCHO
1:2.5
The resulting solution is boiled for 1 hour under a reflux condenser. Butanol (1.5 ~20 mol per of urea) is added with a little xylene water removed and an acid usually phosphoric acid as a catalyst is added and heating is continued. The solution is naturalized and concentrated to a desired solid content.
Urea (1 mol)+formaline (2.5 mol)→resultant
(PH=8, boiling under reflux butanol 1.5 ~20 mol per mol of urea, little xylene)
Resultant= a solid content of modified resins
Properties of urea-formaldehyde resins
- These resins are available in a wide range of colors.
- It is a rigid and insoluble material.
- Its molding is poor heat resistant and discolors and degrades at 800C.
- Urea formaldehyde molding has good insulating properties. Its polymer are very resistant to organic reagents, but they are attached easily by acids and alkalies
- It shows relatively high moisture absorption as compared to phenolic resins, and melamine resins.
- Specific gravity 1.5 gram/cm3
- Tensile strength 7500~11500 lb/ inch2
- Breaking strength 11000~ 17000 lb/ inch2
Application of urea-formaldehyde resins
Urea-formaldehyde resins are used in making molding powder, as an adhesive in plywood and chipboard, used as eliminated plastics, for surface coating, and for crease-resistant fibers.
In textile finishing, it is widely used, in the paper industry and its miscellaneous uses are in the electrical industry, automobiles, and household articles.
FAQ
Melamine formaldehyde resin
Melamine formaldehyde resins are carried out in two operations.The first operation involves the formation of low molecular weight fusible and soluble resins and the second operation involves a curing reaction which leads to cross-linked products. Various types of melamine formaldehyde are produced commercially and are classified into
- Unmodified resins
- Modified resins
1-Unmodified resins
These resins are normally used in the preparation of molding composition and adhesive.
Preparation of melamine formaldehyde resins
These resins are prepared with the help of the following reactions
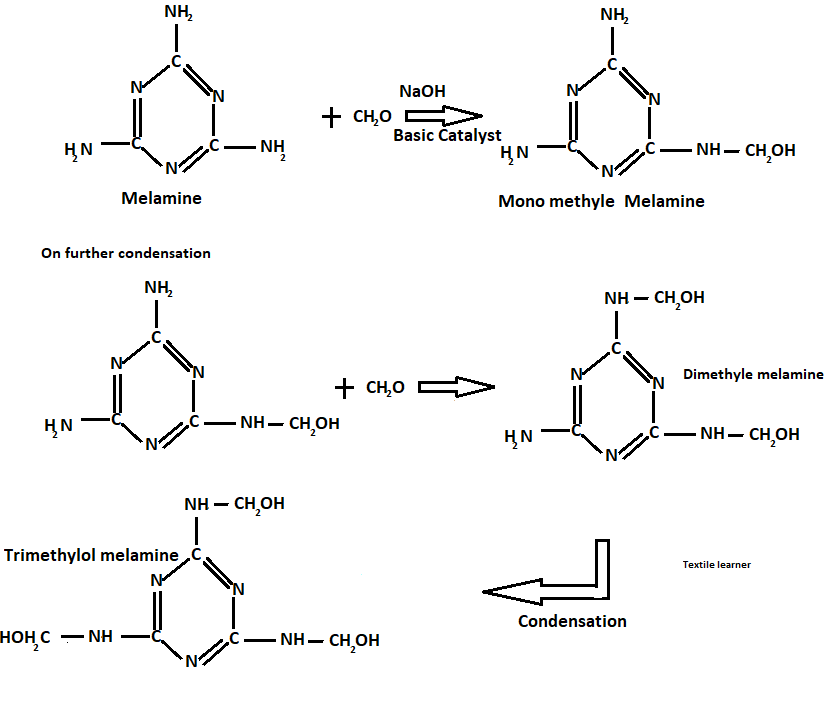
Let’s say trimethyl-ol melamine is R
Hence, after the condensation sheet formation takes place as follows
Resin ( A stage) + Filler(cellulose)+catalyst (TiO2,titanium dioxide) +lubricant( steric acid) → mixed over hot roller → sheet formation take place
B-stage
In this stage, the sheet is grounded and dehydrated (also, removal of water takes place)
R -NH-CH2OH +HN-R-CH2OH → -H2O + RNH-CH2—CNR-CH2OH
After this in stage C cross-linking takes place.
2-Modified resins
These resins are prepared by the following reactions
Melamine + formalin → solution is derived to 80%solid content under reduced pressure (required PH 8~9, 700C, methanol or butanol
Hence, the solid content is known as melamine formaldehyde resins.
Properties of melamine resins
Melamine resins are also called molding powder, or bakelite plastic or urea. The main properties are that these resins show surface hardness and are produced in a wide range of colors when melamine resins are linked together they form an infusible and insoluble coating. Melamine resins are very resistant to organic reagents but they are affected by alkalies and acids, as compared to formaldehyde resins the effect of alkalies and acids is much less
Applications of melamine resins
These are used for surface coating, These are also used as binding material with epoxy, paints, and varnish materials made for the protection of the surface.
Epoxy resin
Preparation of epoxy resins
Epoxy resins are prepared by condensation of excess chloro-epoxy alkaline with dihydric phenol (diphenyl-ol propane) in the presence of alkalies or bases i.e. NaOH.Also, an excess of epichlorohydrin is used to leave the epoxy group on each end of the low molecular weight polymer 900~3000).
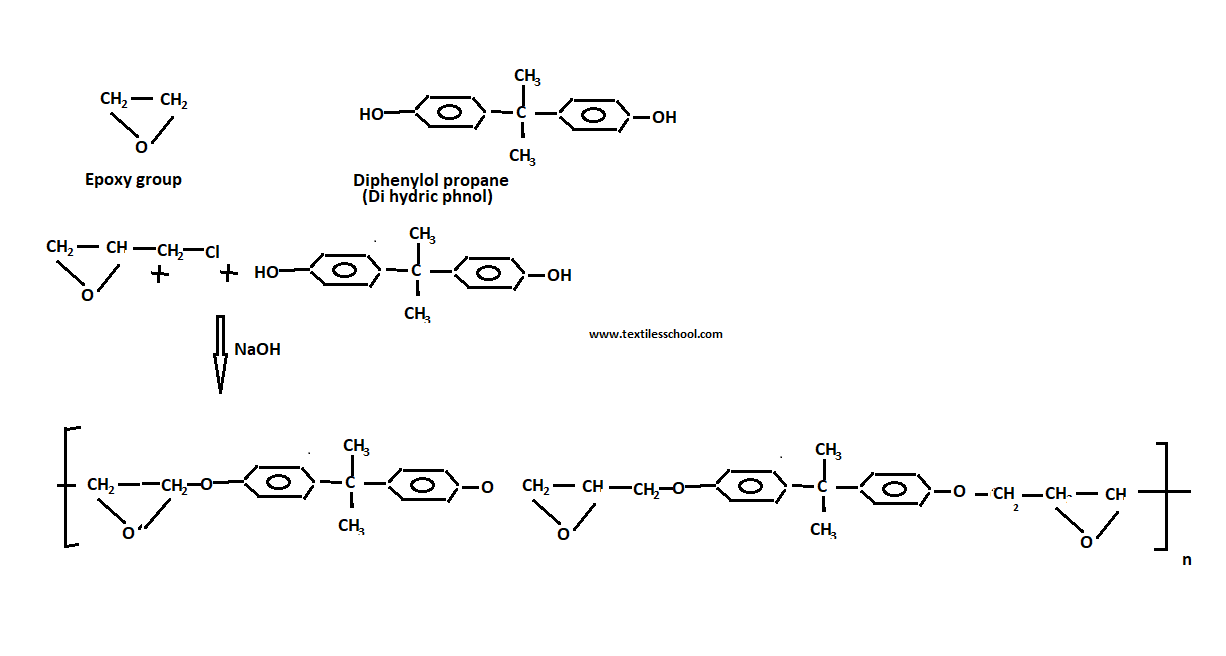
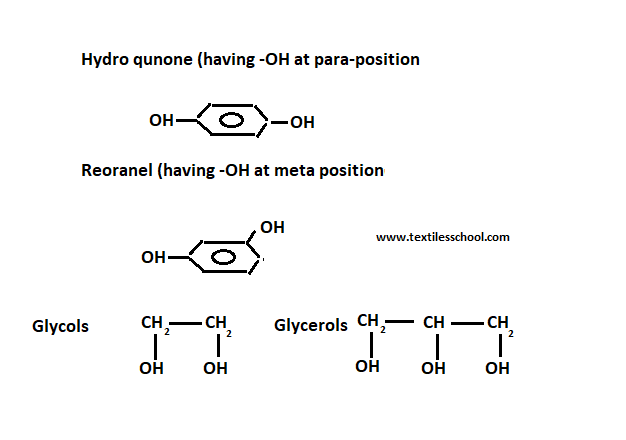
So the polymer is produced cross-linked by heating with a certain amine cross-linking chain. Another hydroxyl-containing compound hydroquinone and resornet, glycols, and glycerol can be replaced by di-phenyl-propane.
FAQ
What is epoxy resin?
Epoxy resin (polyepoxides) polymer which is known for its binding properties is used in adhesives such as Araldite. It is an organic compound containing epoxide groups. Epoxy is cross-linked carbon chain like hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. The epoxy resin is used as typically a two-part, used for repairs, and adhesive.
How to use epoxy resin?
Is epoxy resin toxic?
Poly urethanes
Urethanes polymer contains group -NHCOO- and is formed during the reaction of di-isocyanate and glycol.
(-CNO cyanate, cyanite CN)
I e.
1-4 butane glycol+ toluene di-isocynate
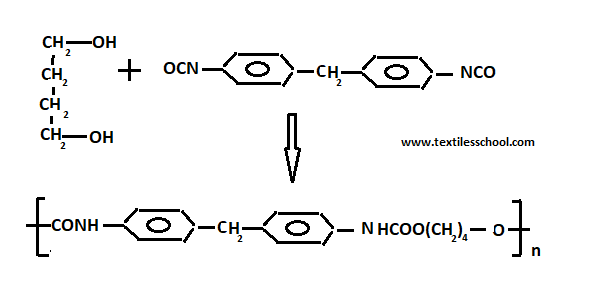
Catalysts based on toluene amine are added to achieve rapid production of foam. Cross-linking takes place to give a thermosetting polymer. The basic intermediate is bifunctional foam is desired and polyfunctional groups are required if rigid foams are to be made i.e. tri-isocyanate and tri-OH group is used.
Poly urethanes can be spun into elastic fibers such as “ spandex“. Also, poly urea foams are used in the construction of interior decoration of buildings.
Alkyd resin
These are polymers derived from alcohols and acid anhydride. Also, these are called glyptic resins. Moreover, It is obtained by heating phthalic anhydride and glycerol at 1800C
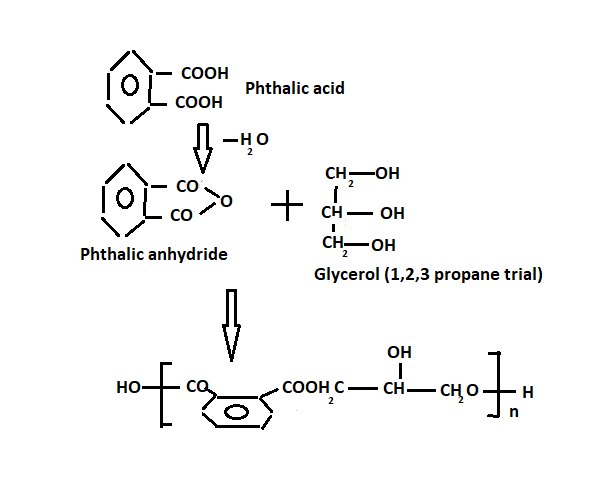
Also, they can be dissolved in a suitable solvent and applied as a surface coating. On heating, the solvent evaporates, and a hard smooth protective surface results, owing to cross-linking the chain. Alkyd is normally used as a binding design and in alkyd paints.
FAQ
What is Epoxy Resin
Epoxy resins are known for their strong adhesive properties. It is highly chemical resistance. They are commonly used in coatings, adhesives, and composite materials. It is used in applications such as electronics and aerospace too.
What is Resin Used for
Resin is used across a wide range of industries and applications due to its versatile properties. It is widely used in manufacturing, construction, and building materials as adhesives and sealants, coatings, composite materials, automotive and transportation as body panels and parts, coatings and finishes, , electronics and electrical components, packaging, art and crafts, medical and dental applications, aerospace and defense, consumer goods, etc.
Resin can be made from both natural and synthetic sources. Its composition varies depending on its origin and use. Here are the materials used to make resin:
Synthetic resins are derived from petrochemicals. Epoxy resins are produced by polymerizing epoxide monomers with a curing agent. They are known for their strong adhesive properties and are used in coatings, adhesives, composites, and electronics. Polyester Resin is made by reacting dibasic organic acids with polyhydric alcohols. They are commonly used in fiberglass products, automotive parts, and construction materials. Polyurethane Resin is formed by reacting polyols with diisocyanates. They are valued for their flexibility, durability, and resistance to abrasion and are used in foam insulation, coatings, adhesives, and flexible plastics.
Natural resin is extracted from plants or shrubs by tapping the bark. It is extracted from a pine tree called Rosin used in varnishes and inks, The Acacia tree’s gum arabic is used in food and pharmaceuticals, and lac beetle’s shellac is used as a wood finish, in food glazes.
What color is resin
The color of resin can also vary depending on factors such as the type of resin (e.g., epoxy, polyester, polyurethane), the presence of additives or fillers, and the curing process Resin can come in various colors, depending on its composition, additives, and any pigments or dyes used. Also due to the types of resin and curing process. These additives are added during the manufacturing process. Common colors of resin are clear or transparent resin, white, black, colored, translucent, and metallic.