Water purification
For the purification of water, several methods are used which include below. Include physical processes such as filtration, sedimentation, and distillation, biological processes such as slow sand filters or biologically active carbon, also chemical processes such as flocculation and chlorination and use of electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light are used. pretreatment may include the addition of chemicals to control bacteria growth and large tanks are used to settle down suspended impurities at the bottom.
Surface water has a risk of more polluted water with a large amount of contamination present.
- physical processes, such as filtration, sedimentation, or distillation
- biological processes, such as sand filters, and active carbon
- chemical processes, such as flocculation or coagulation, chlorination,
- Lastly, the use of ultraviolet light
usually, water is supplied from a municipal supply called municipal household water, which is made pure by treatment.
Municipal treatment of water
The majority of peoples depends on supplies of freshwater resources for drinking and domestic usage. However, as the population increases and also shrinkage of freshwater resources leads to complications with other natural factors such as floods, and climate change. Now a day some countries use saline water(sea water )as an alternative after cleansing. The desalination technique is to purify by removal of salts and minerals that removes salts and minerals from seawater and produces potable le water that is suitable for drinking and domestic use. Vacuum distillation, reverse osmosis, multistage flash distillation, and electrodialysis for saltwater purification. Such processes usually involve higher consumption of energy and are most expensive but these energy crises can be overcome with wind or solar energy are compatible and more suitable for this. Numerous efforts are made to make desalination methods economically viable.
System configurations and improvements
In this method, purification of water is made by following four process
- Setting or sedimentation
- Coagulation
- Filtration
- Sterilization
Sedimentation
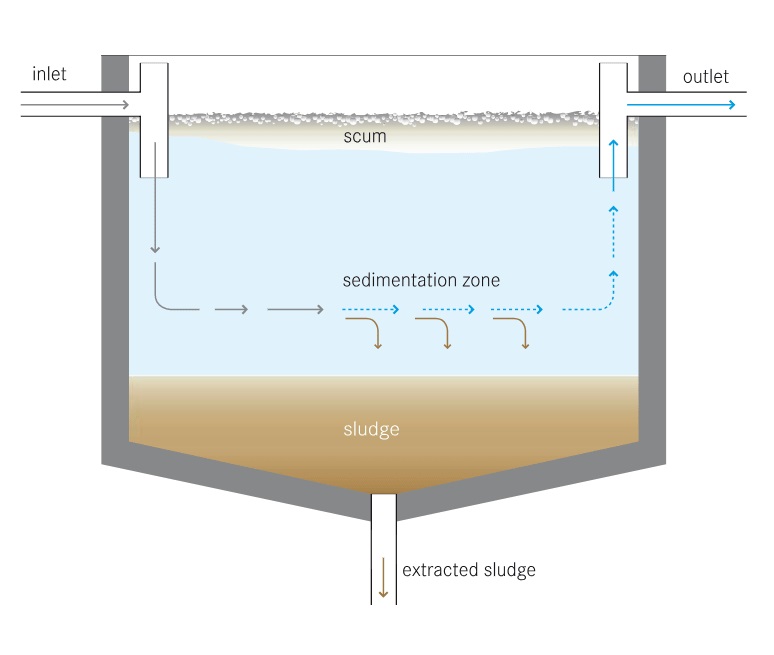
The water from surface sources (rivers, canals, etc.) is brought in a loft tank having a shape slope on one side. Here the slope makes the water stand still and all suspended impurities ( clay and sand) present in the water settle down called sludge.
Sludge
Sludge is a solid (somewhat in liquid form) produced from a range of industrial and municipal, water treatment also, and wastewater treatment.
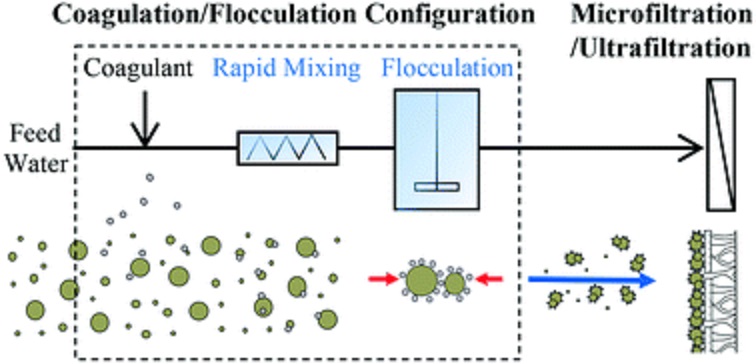
Coagulation
The water sedimentation impurities are coagulated. This is done in a special tank known as a precipitation tank. In this process, water is taken into the aerator which works as a shower, so some impurities of micro-organisms and some organic matter is removed. Then this water is taken into sterilization where a fast-moving fan separates the dust particles. A chemical paste of alumn and lime is also added in water to help the sand particles settle down also colloidal particles of dust are neutralized.
Al2(SO4)3 + 3 Ca (OH)2 → 3CaSO4 + 2Al(OH)3
Al2(SO4)3 + Ca(HCO3)2 → 2Al(OH)3 + 3CaSO4
Ca(HCO3)2 + Ca (OH)2→ 2CaCO3+6CO2+2H2O↓
Flocculants are used as coagulators i.e 0.1 mg /1 lit.
Filtration
This water is taken into a filtration tank. This water has different layers of sand and coal gravel. These layers act as slow filtration bands, it has 3 feet of fine sand bed, 1Foot courser sand, and 1.5 feet of coal gravel. These water filters are very slow giving 2 gallons / Foot2/ hour. These filters are called gravitational filters(Gravity filtration is a method of filtering impurities from solutions by using gravity to pull liquid through a filter). Nowadays rapid filters of 100 gallons/ Foot2/ hour. are used. In advanced countries, bi-flow filters are being used.
coal gravel
Coal Gravel is a crushed granite stone with stunning black stone, it is suitable for numerous landscaping solutions and is one of our most popular is filtration.
Sterilization
The water after filtration has only a few impurities considered clear water but has bacteria.
1-Aeration
As explained above this process is the blowing of air through water. It helps the oxidation of organic impurities and also eliminates CO2, disagreeable color and taste.
The treatment of wastewater is a multi-step process. In industrial and municipal wastewater treatment plants the first step, oxygen is injected during the secondary treatment process. Also known as the sludge process activation, the oxygen is pushed by the pump into the wastewater tank to increase the growth of the bacteria
Also, the Fenton process is an advanced treatment method. The hydroxyl radical (OH-) can be generated from the reaction of aqua ferrous ions with hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). This can destroy toxic organic impurities in wastewater.
2-Chlorination
chlorine is used either as a liquid or in the form of CaCl2, NaOCl after this is free from bacteria (30000→100).
3-Fluorination
Since chlorine causes tooth decay so fluorination is also being used
4-Ozonization
in this method, organized air is passed in a water ozonization tower having large compartments separated by celluloid partitions made of enameled iron through the bottom. These methods include filtration for prominent dissolved substances, also, ion exchange to remove metal ions.
5-U.V rays
Now a day a modern method is used for sterilization. In this U.V rays are used, it is superior because it does not impart any order or tested to natural water. A mercury vapor lamp is used as a source of UV rays.
Disinfection is the last step in water purification. During this process, large and harmful microbes, such as bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, are killed through the addition of disinfectant chemicals. Disinfection also involves a form of chlorine, chloramines or chlorine dioxide. Chlorine is a harmful gas, resulting in some complications associated with its use. So, some water treatment plants use ultraviolet rays or hydrogen peroxide instead of chlorine.
In some countries where people don’t have access to water filtration plants use boiling methods to convert impure water to drink or use. Also, methods of granular activated-carbon filter, distillation, reverse osmosis, and direct contact distillation membrane.
Industrial water purification
In addition to irrigation and drinking uses, industries also consume large amounts of water. Food processing, and textile industries, for example, require water for processing, manufacturing, cooling, heating, washing, and rinsing applications. Such industrial requirement is treated water, also, purification can lead to huge damage, issues may be scaling, corrosion, and deposition, within piping or processing equipment, resulting in a poor quality product. Industrial water purification may involve special techniques such as electro-de-ionization, membrane systems, evaporation, ozone treatment, and ultraviolet radiation. The selection of technologies depends upon the raw water quality and industrial use.
Size and capacity of the water purification plant
The size and capacity of purification of water treatment plants largely vary depending on their usage in household facilities small industries and also on several facilities. Also maybe extend from town to city or even cities. The selection of purification techniques depends upon the sources of raw water used and the quality degree of the purification. Also on the flow rate required, government regulation, capital, operational cost and maintenance costs are involved. This treated water is supplied to the user through pipes, booster stations, and storage tanks.