Warp knitting
Warp knitting is different from weft knitting in the sense that every needle loops its own thread. Machine needles produce parallel rows of loops interlocked in a zigzag pattern, which is called warp knitting.
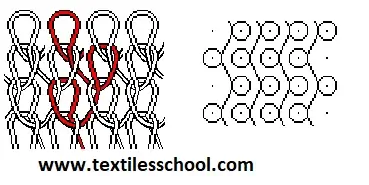
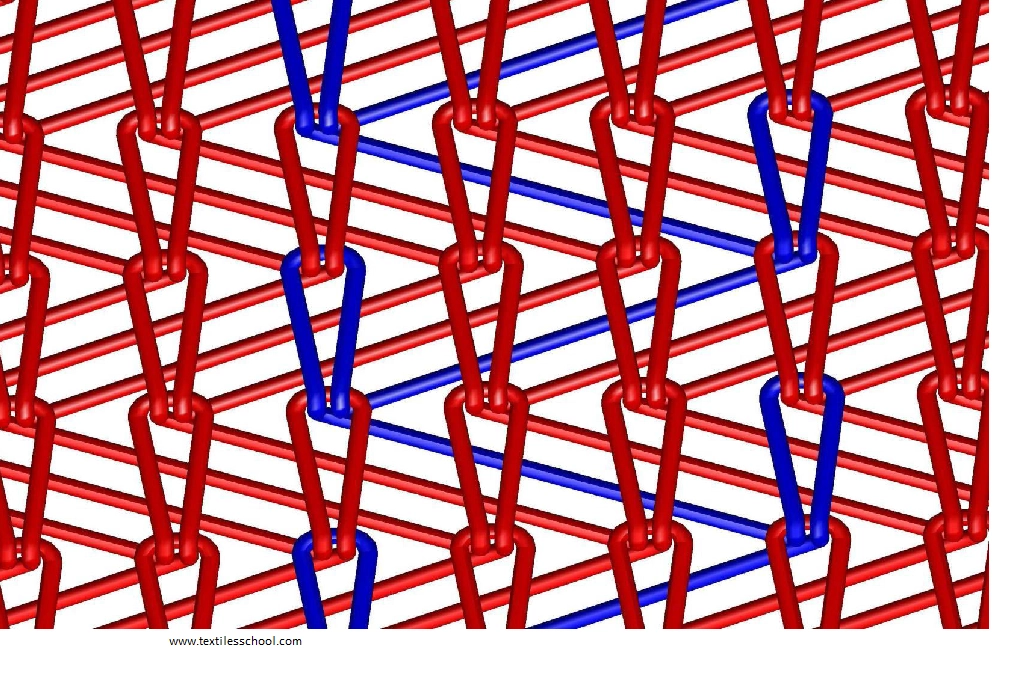
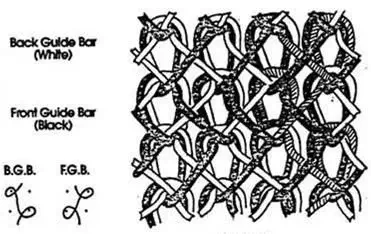
The stitches on the front side of the fabrics appear vertically having a slight angle. The stitches on the backside appear horizontally as floats at a slight angle. These floats are called laps or underlap and are distinguished features of warp-knit fabrics
Types of warp knitting
It is a very fast technique that can produce fabric with a dimensional stability almost equal to that of woven fabric.
There are basically seven types of warp knitting.
- Tricot knit
- Milanese knit
- Simplex knit
- Raschel knit
- Ketten Raschel knit
- Crochet knit
- Weft-insertion warp
All warp-knitted fabrics are relatively easy to sew and resistant to runs.
History of warp knitting
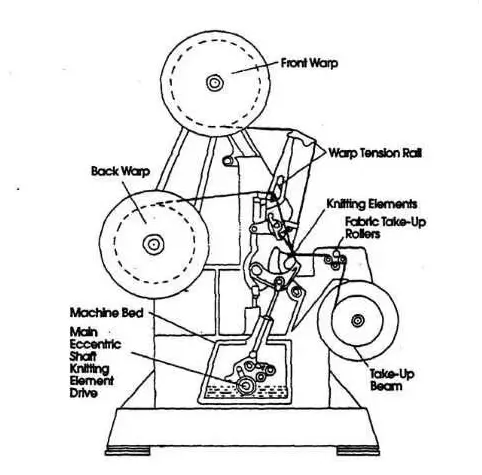
Warp knitting machine
Basic terminologies
- Tricot
- Rachel
- Gauge
- Guide bar
- Needle bar
- Runner length
- Rack
- Inch Quality
- Full set
- Part set
- Positive feed
- Negative feed
- Pattern wheel
Tricot
A type of warp knitting in which needles (spring bearded)are normally used, also, usually one to three warps are used to make fine fabrics.
Raschel
a type of warp knitting in which jacquard and plain fabrics can be made. Also, raschel types of warp knit fabrics are normally coarser than others but can be made in a wide range of fabrics. Mainly raschel machines may have up to thirty guide bars and one or two sets of needles.
Gauge
it is per linear inch of the needle bar to the number of needles. For most warp knits that refers to one linear inch, but can be for two.
Guide bar
A mechanism on a warp knitting machine directs warp yarns to the knitting needles, and their movement is controlled so that patterns can be knit.
Needle bar
A flat metal plate with slots (tricks) cut into it at regular intervals into which needles slide during the knitting process. Runner Length – in warp knitting the knitting of one rack of fabric required a number of inches of yarn.
Rack
A warp knitting measure of 480 courses, the number of inches per rack, it is a judge mark in tricot fabric quality.
Inch Quality
A measure of the quality of warp knit fabric, the number of inches of fabric per rack.
Full set -in warp knitting a term that shows that a guide bar each has a yarn in all guide eyes from the warp.
Part set – a term that indicates that all guide eyes in a guide bar do not have a yarn from the warp.
Positive feed – It is a device used for measuring the yarn tension in the warp of fabric in knitting.
Negative feed – when the yarn is pulled off the warp beam by the knitting action of the needles during the loop-forming step.
Pattern wheel – a cylinder or wheel upon which a pattern chain is placed which has links of different heights so as to move the guide bars
throughout its pattern.
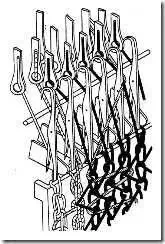
The Warp knitting machine elements
Warp beams
- Firstly, yarn is supplied to the needles in the form of warp sheets.
- Each individual warp sheet is usually supplied from its own beam, which may consist of several section beams.
- Also, the number of beams used on a machine is normally equal to the number of guide bars.
- To ensure uniform conditions of warp feed and also, tension, the ends are supplied from flanged beams attached to shafts which turn to unwind the warp sheet in parallel formation.
- For the convenience of handling, some beams may be attached to a beam shaft to achieve the full width of the warp sheet, for example,
Warp sheet width
- A full-width beam warp sheet 84 inches basically (213cm)
- Two beams also, each width of 42 inches (106 cm)
- Maybe also, four beams each width of 21 inches (53cm)
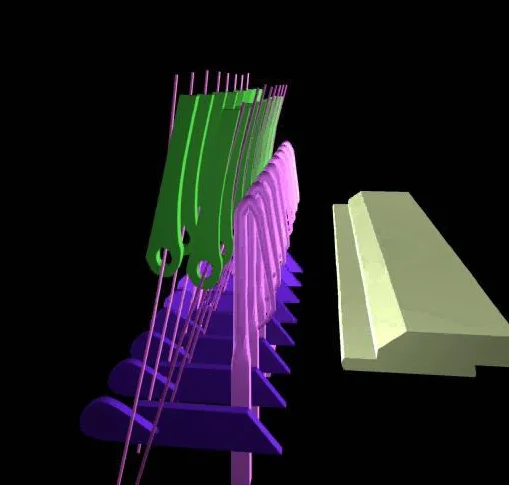
Guide bars
- The guide bars extend across the complete width of the machine and their function is to wrap yarn around the needle (i.e. feed).
- Each guide in the guide bar overall is usually provided with a single end of the yarn. So, warp knit machines are usually equipped with two or more guide bars.
- Each guide bar is usually supplied with a warp sheet from its beam shaft to meet its requirements of the rate of warp feed and also, threading for its particular lapping movement.
Needle bar
- Needles, either mounted individually or in leads, are clamped to the needle bar which extends across the complete machine width.
Sinker bar
- Sinkers are positioned between each pair of needles in the needle bar and provide fabric control during loop formation.
Warp knitting action
Elements
Basic warp-knit actions
- Spring beard needle
- Latch needle
- Compound needle
Design variables
- Yarn characteristics
- Threading
- Under lap length and position
- Number of bars
- Fabric enhancement
Fabric classifications
- One bar
- Two bar
- Three bar
- Multiple bars
Warp knitted fabric notation
- Verbal
- Graphic
- Numerical
- Diagrammatic
The warp knitting machine classification
Tricot machine
A tricot machine is a warp knitting machine that basically uses a single set of bearded or compound needles.
Also, the fabric is removed from the needles at approximately 90 degrees.
The tricot machine tends to have a fine gauge (28-32npi) and fewer guide bars (2,3 or 4), also, producing a simple and fine structure.
Two-needle bar raschel machine
The two-needle bars Raschel machine basically, is a warp knitting machine equipped with two sets of vertically mounted latch needles.
Also, the fabric is removed from the needles vertically downwards between the two needle bars.
Occasionally, guide bars with two partly threaded may be supplied from the provided they make lapping movements from the same full-threaded beam of the same extent to each other while directions in opposite moving.
The minimum number of warp sheets and also, guide bars for commercially acceptable structures is usually two.
Construction of warp-knitted fabric
Single guide bar fabric
Warp-knitted fabrics, in which all the yarn follows at least exactly the same lapping movement. So, these are normally made with a single guide bar controlling the yarns.
These fabrics have little commercial importance because of their low cover and lack of stability
Two guide bar fabric
The use of two guide bars gives a wider scope for patterning than is available with single guide bar fabrics. Also, these fabrics form the basis of commercial trade, using continuous filament materials in most cases.
Part-threaded fabric
The guide eyes of one or more guide bars are basically not all threaded yarn, only a part of them are threaded.
The part-threaded fabric can produce some interesting surface appearance, such as relief or openwork structure.
So for one width repeat, the guide bar threading is usually shown between the needle spaces in its correct relative position of the design. Also, at the first link with “|” representing a threaded guide and “·” representing an empty guide.
Basically, wales will be drawn together where underlaps pass across between them. Also, it will separate at points where no underlaps cross-producing net pillars in the former and net opening in the latter. If a guide bar is full-threaded which knits at every course is also used, the effect will still occur in the form of a relief or cord instead of a net.
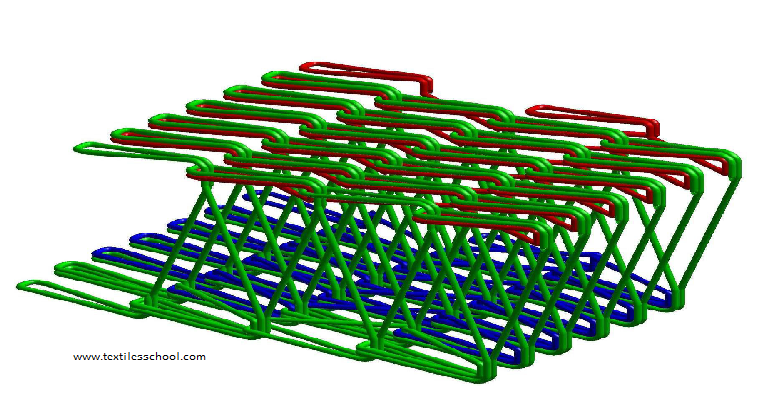
Double needle-bar fabrics
- As with weft knitting, warp knitting can also work with two sets of needles and produce double needle-bar fabrics.
- The most popular double needle bar fabric is the pile or velvet effect also produced by splitting the space fabric into two pieces.
- The un-split space fabric can also be used as a technical fabric such as a substitute for the foam. It can produce the tubular form of fabric for techniques used such as vascular tubes, bandages, etc.
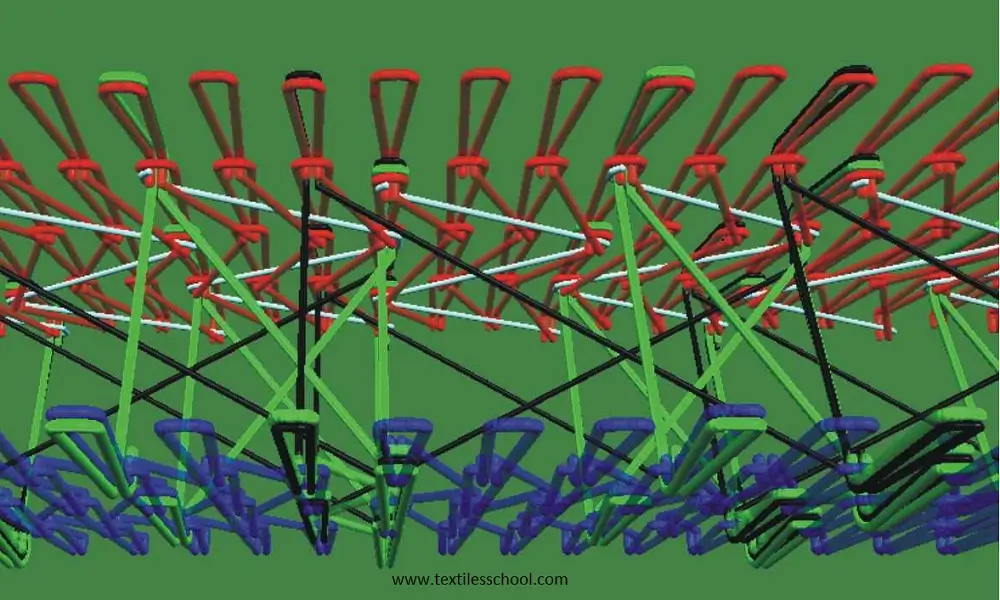
Simulated structures from single needle bed warp knitting machine
Structures from double needle bed machine
Simulated fabrics, produced with 2 needles & 5 guide bars.
Warp & weft comparison
Warp knitting and weft knitting by all means are the two major differences in knitting. Firstly, single yarn requires in-weft knitting. Also, in warp knitting, one yarn for every stitch is used. Weft knitting mostly is done either by machine or hand and warp knitting is done generally by machine.
Definition
comparatively, warp knitting is a knitting type in which the yarn loops in zigzags with the length of the fabric. While in weft knitting yarn running crosswise or in a circle.
Structure
In weft, knitting knit structure is produced horizontally when each yarn loop is following to other in the needle bed.
While in warp knitting the yarn is zigzag along the fabric width.
Properties
Warp is Less elastic than weft knitting. More run-resistant than weft knitting. Fabric is denser than weft knitting. The type and weight of yarn are prominent in the type of fabric that is produced.
While in weft knitting fabric is more elastic, comfortable, warm to wear, and shrinks easily. Also, depending on the yarns used required properties can be achieved.
Machine
Weft knitting machines can generally be classified as circulars and flats. Basically, this classification is based on their needle bed arrangement and frame design. Also, weft-knitted fabrics are produced in either flat form or tubular.
In warp knitting, the warping process is essential and also, and the fabric is produced flat and along the width.
Fabric applications
Hence, extremely versatile in the pattern. Good air and water permeability for warp knitting compared with weft knitting fabric, also, good crease resistance, durability, dimensional stability, strength
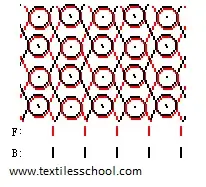
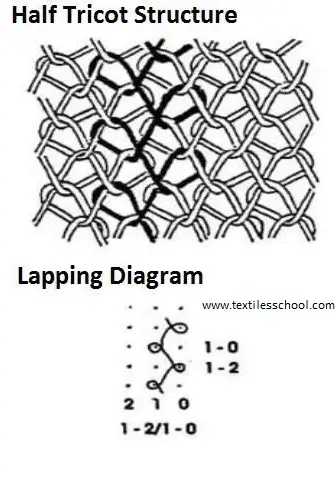
Warp knit structures half tricot
Full tricot
Locknit
Standard Two Bar Fabrics
Tricot Jersey (Full Tricot)
Front Bar 1-2/1-0/
Back Bar 1-0/1-2/
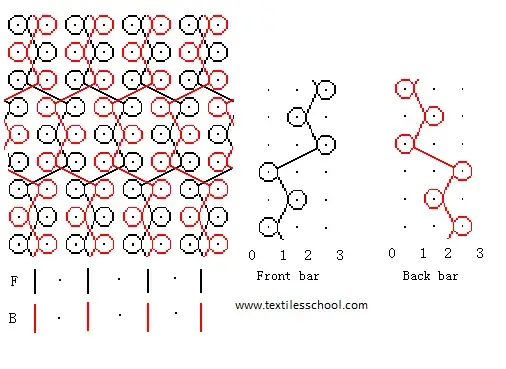
Locknit
Front Bar 2-3/1-0/
Back Bar 1-0/1-2/
Reverse Locknit
Front Bar 1-2/1-0/
Back Bar 1-0/2-3/
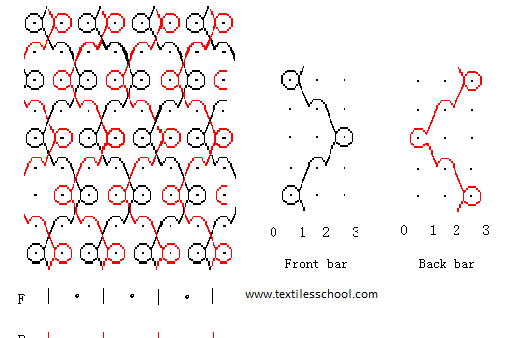
Loop Raised
Front Bar 1-0/3-4/
Back Bar 1-0/2-3/
Sharkskin
Front Bar 1-0/1-2/
Back Bar 3-4/1-0/
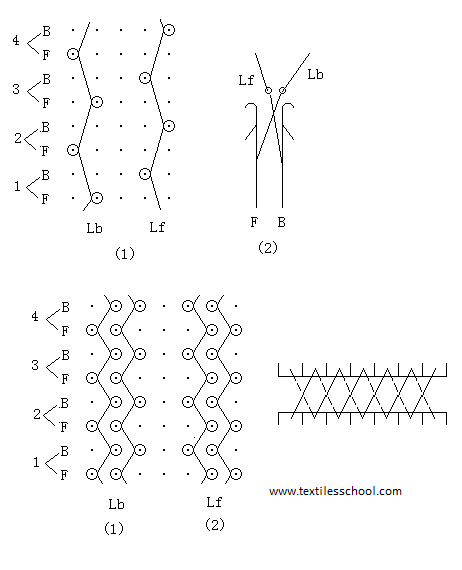
Satin
Front Bar 3-4/1-0/
Back Bar 1-0/1-2/
OR
Front Bar 4-5/1-0/
Back Bar 1-0/1-2/
Queens cord
Front Bar 1-0/0-1/
Back Bar 3-4/1-0/
OR
Front Bar 1-0/0-1/
Back Bar 4-5/1-0/
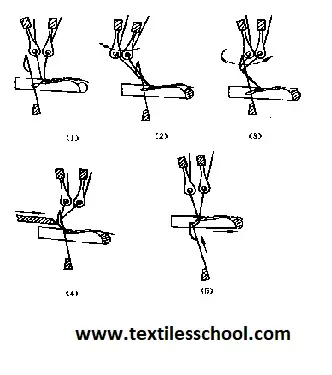
Diagram showing laying in yarn to form designs:
Some guide bars are left empty
Characteristics of warp knit fabrics
- Extremely versatile with yarn rigid to elastic and in pattern effects
- Cannot be traveled
- Good air and water permeability
- Good crease resistance
- Good drapability
- Good dimensional stability
- Good strength