The Dyneema brand is materials innovation at the leading edge curve. Dutch chemical company used a generic Dyneema brand name “DFC” ( Dyneema Composite Fabric) in the late 1970s for all of its composite products that incorporate UHMWPE. Let,s explore Dyneema (UHMWPE) that’s changing the way we think about strength and durability. Here we’re diving into the fascinating world of Dyneema a fiber called the world’s strongest fiber from its history to the science behind it. Dyneema thread is a Marvel of modern science boasting Incredible strength to weight ratios that surpass even steel intrigued. Let’s discover what makes Dyneema a Marvel of material engineering and unravel the science behind this exceptional fiber. Dyneema fiber is ideal for applications where lightweight and strength are paramount. Dyneema fabric is changing the game in industries from Sports to safety.
Benefits:
- Extremely resistant to UV light, chemicals, and moisture.
- Lightweight with maximum breaking strength gives extra protection.
- Military Armoring
- Cut resistance
- Flexible
- Comfort
- Resistance to puncture
- Life Protection
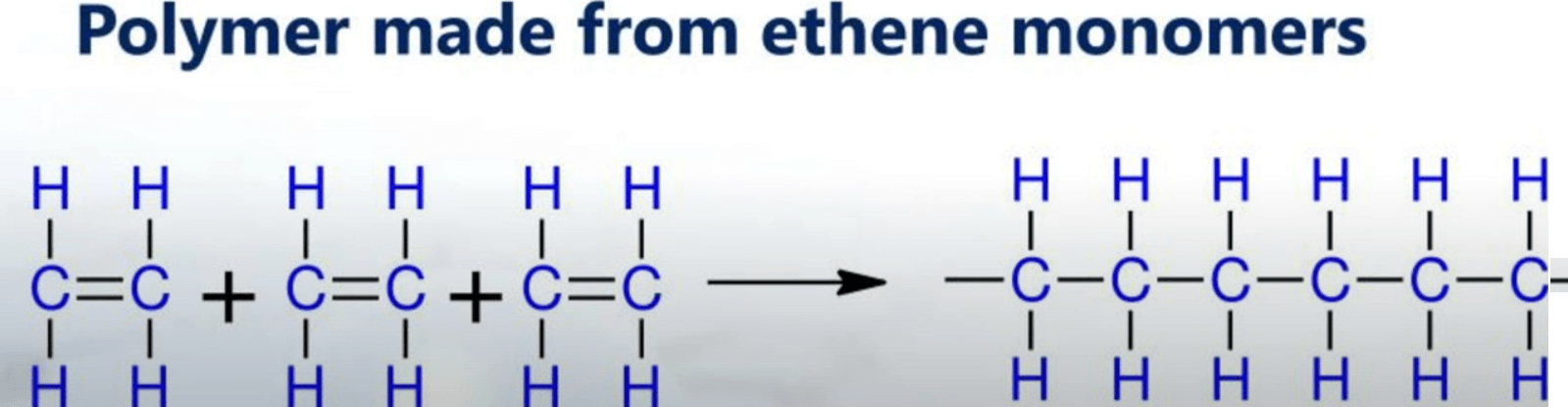
To understand Dyneema we have to start with its building block ultra high molecular weight polyethylene or UHMWPE. Dyneema’s story starts with a gas called ethylene a simple natural gas that is processed in polymerization. Polymerization is the process of linking these ethylene molecules together like beads on a string.
This chain of ethylene forms polyethylene a material you probably know from plastic bags and Bottles. However, UHMWPE is special it has super long chains of polyethylene millions of molecules long these extra-long chains give UHMWPE its Incredible strength and make it the perfect ingredient for Dyneema
- You may also like the post “Classification of Textile Fibers“
- You may also like the post” What is an antimicrobial textile?“
How Dyneema Fiber Made
Dyneema fiber made from simple ethylene natural gas is processed in plants through polymerization to make polyethylene for the formation of Dyneema powder. We use this polyethylene as a raw material, next the powder is dissolved in a solvent a gel-like substance. Then heated in an extruder, using a gel spinning process. To disentangle the molecules the heated substance is forced through a squeezing tube or plate with hundreds of tiny holes at which point the resulting elongated molecules begin to resemble a fiber.
These gel strands are pulled and stretched the UHMWPE chains within them align themselves in a specific direction. This alignment is crucial it’s what gives Dyneema its Incredible strength. The solvent is then removed leaving behind solid fibers of pure highly aligned UHMWPE.
You may also like the post “What does Microfiber Mean?”
These Dyneema fibers are incredibly strong for their weight but the journey isn’t over yet to take things even further. These already impressive fibers undergo an additional process to become dyneema UD which stands for unidirectional. The importance of chain alignment for strength well Dyneema UD takes it to a whole new level through a specialized manufacturing process. The UHMWPE chains and Dyneema UD are aligned not just within each fiber but also across multiple fibers. Think of it like weaving together millions of tiny perfectly straight threads. This unparalleled level of molecular organization unlocks Dyneema’s full potential resulting in a material with an astonishing strength-to-weight ratio. Dyneema is up to 15 times stronger than steel at the same weight. So we’ve got this incredibly strong lightweight fiber what do we do with it the possibilities are practically endless.
The world’s strongest fiber Dyneema
When high-strength Dyneema begins to take shape then we can define what is Dyneema. Dyneema is made from ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene a synthetic fiber. This polymer is part of the poly family but differs from other members of the family due to its molecular weight and strength. Now before knowing more about Dyneema here we talk about what is polyethylene. Polyethylene is a polymer made up of repeating ethylene units as in the picture. Routine polyethylene is found in everyday life items like plastic bags and Bottles having a molecular weight of 100,000 to 500,000 grams per mole. Whereas ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene is found in Dyneema with molecular weights between 3 to 6 million grams per mole. Higher molecular weight refers to the total mass of the atoms in a polymer molecule. The Dyneema ultra-high molecular weight means its polymer chains are exceptionally long.
- You may also like the post “Some Sustainable Fibers“
- You may also like the post “Textile Carbon Footprint“
These Chains give it super strength durability and resistance. These interactions make the fiber incredibly strong. Now guys we discuss the historical timeline of Dyneema’s invention. Dyneema’s Journey began in 1963 when Dutch scientist Albert Pennings discovered ultra-strong polyethylene fibers while working at Dutch State mines in the Netherlands. Throughout the 1970s and early 1980s, the company Dutch State Mines invested heavily in refining the production process. By 1978 they developed a scalable gel spinning method. And in 1990 Dyneema was officially launched into the market.
Various Grades of Dyneema
Fibr XL Bio-based Dyneema
Bio-based Dyneema is produced as a bio-based ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene fiber from the wood pulp by-product industry. It is a sustainable resource to produce renewable ethyl,e,ne feedstock. This bio-based Dyneema is identical to the fossil-based yarn.
SK99 for ultimate strength
Dyneema® SK99 has a 20% more strength advantage than SK78, but the same level of creep and elongation characteristic as SK78. Sk99 has an unmatched strength-to-weight ratio with ultimate performance core material.
DM20 for Minimum Creep Performance
DM20 Dyneema is used in deep water rope developed for offshore use. Its density is slightly lower than SK78 but has advantages with zero creep. Also used for static load applications such as rigging standing.
3G12 for Maximum Cut Protection
3G12 Dyneema® fibers that have the choice for cut-resistant gloves. In the best-protected hands industry, Dyneema® 3G12 (Diamond Technology) continues to meet modern requirements. Offering durable and dexterous gloves available to ensure that workers’ hands stay safe.
SK78
SK78 Dyneema has become the standard grade. It is durable and resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and UV light used by many reputable manufacturers. Its strength is almost the same as SK75 but offers improved creep characteristics than its previous.
SK75
Dyneema grade SK75 is still available, it used as a reference for many years.
SK60, SK62 and SK65
SK60, SK62, and SK65 are first-generation Dyneema prepared in Japan. It has 20% lower strenth than SK75 and SK78
SK38
An economy-grade or lower-grade generic Dyneema DCF uses cheaper products with low elongation and strength as compared with modern Dyneema.
key characteristics of Dyneema
Dyneema is used in a wide range of applications where strength durability and lightweight design are critical. You’ll find Dyneema in high-performance ropes for sailing and climbing where its strength and resistance to abrasion are invaluable. It’s used in cut-resistant gloves to protect workers in industries like manufacturing and construction. It’s so lightweight yet strong Dyneema fabric is ideal for body armor providing crucial protection for law enforcement and military personnel.
Dyneema helmets are used in tactical police teams like SWAT. These helmets made with Dyneema hard ballistic resistance material are stronger and lightweight than previous materials. Dyneema is used as lifeline gate hooks due to its lightweight.
Dyneema is more than just a fiber it’s a testament to the power of human Ingenuity by understanding the properties of materials at the molecular level. We can create things that are lighter, stronger, and more durable than ever before as research and development continue. Innovative applications for Dyneema in the future from lighter and more fuel-efficient vehicles to more resilient infrastructure. Dyneema has the potential to revolutionize Industries and improve our lives in countless ways. So the next time you see something incredibly strong yet surprisingly lightweight. Remember the incredible science of Dyneema the fiber that’s changing the world one strong thread at a time.
Superior strength: Dyneema isn’t just strong it’s packed with unique characteristics. It is 15 times stronger than steel when compared on weight to weight basis.
Lightweight: It can float on water having a density of only 0.97 grams per cubic cm.
High Crystallinity: It has an 85 to 95% crystalline structure, ensuring maximum strength.
Durability: It is highly resistant to chemicals, UV light, and abrasion.
End Uses and Future Potential Dyneema
Dyneema is used in a wide range of applications and Industries. For example, it is used in lightweight ropes, crane ropes, fishing nets, tents, bulletproof vests, ballistic helmets, armor vehicles, climbing ropes, outdoor gear, futures, and implants. Dyneema is used as a lifeline Dyneema gate hooks
The Legacy of Dyneema
From its humble beginnings in a Dutch lab to becoming the strongest fiber in the world Dyneema is not just a fiber it’s a revolution.
FAQ
Is Dyneema washable?
Yes, Dyneema is washable but avoid machine washed and machine dryer. Use hand washwash and air-dried to prevent shrinking or damage. Use warm water and laundry detergent in a bucket or bathtub. Tents and tarps should be air-dried while set up, and backpacks and other accessories should be line-dried. Before going to the store make Dyneema gear completely dry.
Is Dyneema waterproof?
what size is Dyneema for the line?
-
Replacing an existing line
If you’re replacing an old line, you can match the diameter exactly of the line you already have.
-
Block size
Most blocks allow you to use a slightly thicker or thinner line.
-
Boat size
If you have a larger boat or rig, you can use a double-braid line with a Dyneema core for strength.
-
Lifelines
Some rope manufacturers recommend a minimum diameter of 4 mm for Dyneema ropes used for lifelines.
Here are some approximate breaking loads for different diameters of Dyneema rope:
- 6 mm: 3,200 kg
- 8 mm: 5,300 kg
- 10 mm: 7,900 kg
- 12 mm: 12,300 kg