The raw cotton fibers are removed from the seeds after picking cotton. The process of removal of cotton fiber from the seed and also, the removal of impurities is called ginning of cotton. Due to the mechanical picking of cotton, there is much trash along with cotton nowadays. So the processes involved in ginning are drying, cleaning, and separating the seed from cotton.
In the past before the 18th century, ginning was done with a manual process called “hand ginning”. Hand ginning involves hand-held tools like paddles and wire brushes to remove fiber from seeds. Workers manually separated fibers by repeatedly beating cotton balls and brush to collect lint. This manual process was labor and time-consuming with a lot of manual effort.
Who invented the cotton gin?
In 1794, inventor Eli Whitney from the U.S.A. patented the cotton gin, a machine which considered a revolution in the cotton production process of removing cotton fiber from seeds. Up-to-the mid-19th century, cotton had become America’s leading export
Terms used in cotton ginning
Some terms are used in the ginning of cotton as under
1. Lint
Lints are long raw cotton fibers removed from cotton seeds in ginning process, afterwards, these fibers are used in cotton yarn and fiber manufacturing
2. Linters
These are very short fibers that are not removed from seeds in the ginning process but are special delinters machines at cotton seeding mills
3. Ginning out turns
It is the percentage by weight of lint. Its ranges from 30~40%
Types of cotton ginning
Cotton supply chain ginning is a critical step, as has a significant effect on quality and fiber produced values. Modern ginning uses advanced machinery and technology while delivering the highest standard of quality removal of fiber from seeds and removing impurities from fiber. This cotton gin material after processed is sent for further use as spun into yarn and next woven into fabric and various cotton products, etc.
Cotton ginning processes are of two types used at present
- Saw cotton ginning
- Roller cotton ginning
Saw cotton ginning
Saw ginning machines consist of revolving shafts bearing, about 80~120 saws about 18″ diameter. Also mounted 3/4″ apart from each saw has about 264~282 particular shaped tooth around their circumference.
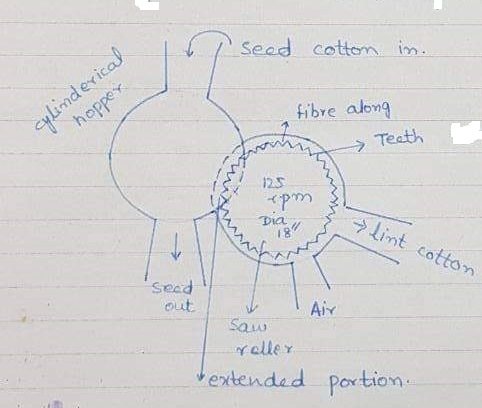
The saws project through a steel grid or metal rib at the bottom of the hopper. The spaces between the bars of the grid are in such a way as to resist the passage of the seed while allowing the saw to revolve freely. Thus when seed cotton is dropped into the hopper, the fibre is held by the teeth of saws and carried through the grid. The fibre is removed from the saws and the seed slides down and is collected.
The saw ginning is divided into two following main classes according to methods of stripping fibers from the saws.
- Brush ginning of cotton
- Air blast ginning of cotton
Brush ginning of cotton
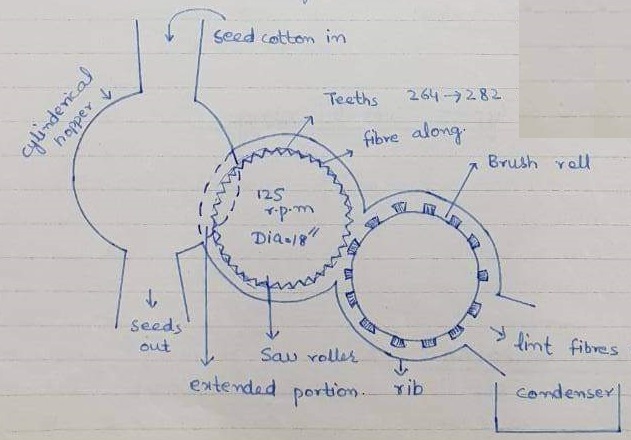
In brush ginning a large cylinder up to 18 inches in diameter and carrying about 30 lines of thin brushes, rotate at a much higher speed than the saws. The fibres are swept off and carried along the drum. Condenser by strong air stream caused by the high speed of brushes.
Air blast ginning
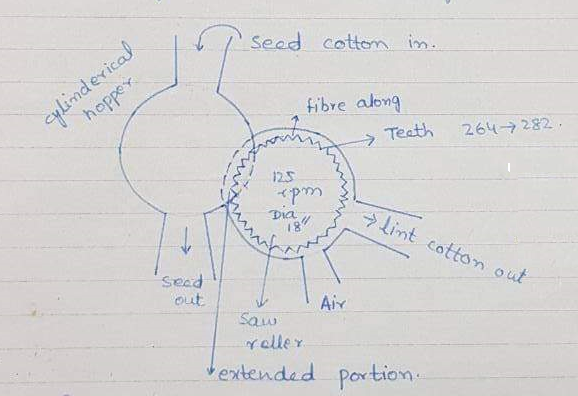
In air blast ginning the fibres from the teeth are removed by blowing air through a nozzle placed close to saws. In most, air blasts the trash tends to fly off the saws before the lint is stripped out. Also, the shape of the nozzle is in such a way that they do not rejoin the steam of air but settle down.
Roller ginning
The machine used for roller ginning nowadays is called the Maccrathy ginning machine. Further, this machine consists of rollers, a stationary knife connected to a crank by means of a crank leg, and a moving knife.
The stationary knife is held in a vertical position against the leather roller while its lower edge is on the center line of the roller. The moving knife reciprocates up and down across the lower position of the leather roller and stationary knife. While the leather roller has a diameter of 6.5 inches and operates at 225 r.p.m.
Firstly seed cotton is fed into the hopper and at the bottom of the hopper, the seed cotton is pushed towards the leather roller by the rough surface of the leather roller. The surface of the roller is made rough by gluing strips of cotton in a spiral around the roller.
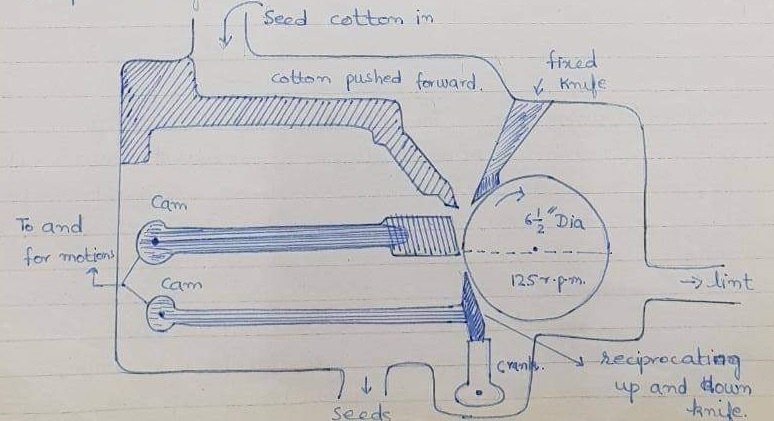
The clearance between the stationary knife and leather roller is so adjusted that only fibres are allowed to pass and seeds are held back by the stationary knife.
As well as the moving knife goes up it pushes the seeds and seeds are dropped down to the bottom of the hoppers several strokes of the moving knife are required to gin each seed. The lint is removed from the roller by a stationary doffer. Whereas roller ginning is normally used for the ginning of extra staple length.
Advantages of saw cotton ginned
- Saw-ginned cotton is well open and well separated.
- Saw-ginned cotton has less waste as compared to roller-ginned cotton.
- Saw ginned cotton is brighter in appearance.
Disadvantages of saw cotton ginned
- Saw ginned cotton easily suffers fibres damage.
- Increase in short fibre content.
- Increase in Neps
Advantages of roller cotton ginned
- Roller ginned cotton is not easily suffered any damage in fiber staple.
- Secondly, roller-ginned cotton is lumpy and opened properly.
Disadvantages of roller cotton ginned
- It contains a large amount of waste such as dust, vegetable branches, and leaves because the setting point of roller ginning is such that impurities come in contact with raw cotton fibers by means of a leather roller.
- Roller-ginned cotton is dull in appearance
- The moisture of the seed is mixed up in processing.
Faults of cotton ginning
- Neps formation
- Seed in cotton fibers
- High waste
- Ginning cut fibre
Cotton ginning practices in the world
For the ginning of seed cotton, both processes saw and roller ginning are in existence. But due to the low operation of roller ginning it costly process. About 70% of cotton is ginned by the saw-ginning process.
How to get rid of moisture in cotton ginning
when seed cotton arrives in ginning factories it contains a large amount of trash, and many have excessive moisture so it is difficult to get rid of the trash content they stick to fibers. At 7~9% moisture machine does its job best hence cotton is dried up to this moisture. But over-drying reduces its spinnability. Hence great care is taken in this respect.
In some countries, drying is done directly under direct sunlight. The seed cotton spread on the ground and will be left there for the whole day. Then manually or mechanically conveyed to cleaner attached to the ginning machine.
Cleaning is usually of two types
- Feeder extractor and cleaner
- Willows
The main function of these machines is to feed the cotton seed into the machines, soften the cotton, and extract trash to some extent. Afterwards, separation of fibres from seeds they are taken to a pressing unit
Bale pressing

Three types of machines are used for pressing bales, basically depending upon the density in which they press usually, the modernized form is the hydraulic press. Bale weight ranges from 150 to 380 kg varying from country to country. lastly, its production varies from 12 bales per to 60 bales per hour if considering 150 kg bale weight.
FAQ
Why it is called cotton ginning?
When was the cotton gin invented?
In 1794 Eli Whitney the USA inventor in October 1793, a mechanical ginning machine to separate cotton seed from lint or fiber. The first ginning of the cotton machine was patented by Eli Whitney in March 1794. This machine consists of a wire screen and wire hooks to pull fiber from the seed surface.
What did the cotton gin do
Eli Whitney’s invention of the cotton gin machine improved the seed and fiber separation, but cotton still needed to be picked by hand. Since machine ginning boomed the rise of the cotton economy in the U.S. South. This increased the demand for cotton hence the production. So, the need for slave labor in the U.S. South badly influenced slavery.
How did the cotton gin affect slavery?
The invention of Eli Whitney’s cotton gin largely expanded the area of labor across the United States South. This labor work was fulfilled through slaves to increase profitability. So, cotton ginning and growing became more profitable for the enslaved which increased their demand for labor and land.
Where was the cotton gin invented?
In the United States, Eli Whitney 1973 invented a machine to collect fiber (lint) from seed cotton called a cotton ginning machine. It consists of a wire screen and wire hooks to pull fiber from the seed surface and brushes to remove loose fiber to prevent jam in the machine.