Cotton plant fibre is fluffy and soft, and grows in a ball as a protective cover is natural fiber. The fiber is spread around the seeds in a cotton ball on the cotton plants. Cotton is an important textile fiber. It is the backbone of the world textile economy. Three-quarters of world textile fabric production is made from cotton. Cotton is the most common natural fiber and is widely used in the world. It is no doubt a king of the naturally known fibers.
Cotton is cool and breathable fiber and can hold moisture up to 25% of its weight. cotton is the purest form of cellulose and is found in the most available natural polymers.
Cotton is not synthetic fiber it is a vegetable fiber like other material fibers, and its essential part is cellulose. Cellulose is the condensation polymer of glucose i.e. in which glucose units are linked together to form a molecular weight of 10,000 to 20,000.
Cotton fibres are the purest form of cellulose naturally found polymer. Also, about 90% of the fiber is made of cellulose. Euro bank notes are made of pure cotton due to its distinctive feel and durability.
The story of cotton/ History of cotton fiber
Before 3000 B.C. cotton was first cultivated around the Indus River valley (Now in Pakistan). Later on, South African, Chinese, and Egyptian cultivation started and spun and woven into fabric and cloths. Somehow there are rags of cotton found in caves which were estimated around 7500 B.C. old. Additionally, we can say that cotton fibre is as old as the age of a human being.
Cotton fibres are obtained from cotton seeds by the ginning process. The cotton seeds are obtained from cotton balls grown on cotton plants. The cotton plants are a genus in the “Gassypium” family of the mallow family.
Cotton shrub plants are grown in tropical and subtropical atmospheres in the USA, Mexico, Egypt, India, Pakistan, Afghanistan etc.
Cotton is a staple fibre which means it has varying fibre lengths. It has a staple length of about 0.8 inches to 1.40 inches
What are cotton fiber types?
Cotton fiber generally has Four types commercially cultivated worldwide, including the genus Gossypium name as.
- Hirsutum (upland cotton)
- Barbadense(African cotton)
- Arboretum (subcontinent cotton)
- Herbaceum(Egyptian cotton)
1- Gossypium hirsutum
It is most of the cotton production about 90% consists of Gossypium hirsutum, also known as Upland cotton. Upland is a short fibre compared to other species. It is used mostly in high-quality products and requires a purity level.
Upland cotton is produced 95% in the central USA and Mexico tertiary.
2- Gossypium barbadense
Gossypium barbadense is the second most produced type of cotton fiber. It has an extra-long staple fiber of cotton and is used in the finest quality of fabric in the world. Mostly named Pima cotton is mostly produced in South America.
3- Gossypium arboretum
Only 2% of cotton production of this type is cultivated. Gossypium arboretum commonly known as tree cotton. It is found mostly in India and Pakistan. It is a short to medium staple used in normal weaving.
4- Gossypium herbaceum
Gossypium herbaceum is known as levant cotton. It is mostly produced in the Nile River in Egypt known as Giza’s extra-long staple cotton. It is globally produced by about 2%. Also used in fine-quality fabric and garments.
Growth of cotton fiber plant
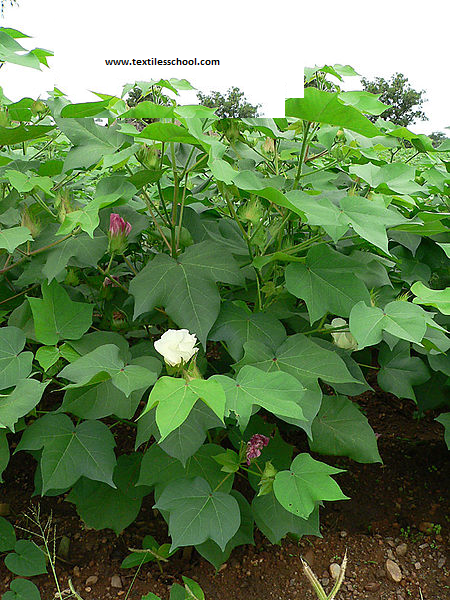
Cotton plants are grown in rows as a crop. While Cotton balls are grown on these plants and through which cotton fibers are obtained.
The cotton plants are 3~6 feet high and 0.5 to 2 inches in cross-section. Also, the shape of the cotton plant is pyramidal. The cotton stalk has main stalks approximately 1″ to 2″ in diameter, further near the base with a leaf 2″~3 ” along the stem. From the axis of the leaf called nodes, two branches grow
Also, the side structure of the cotton fibre plant is divided into two categories.
- Vegetable fibres
- Fruiting branches
Vegetable branches
From the lowermost 2~3 vegetable branches are formed which further are inclined 300 to 450 to the perpendicular axis.
Fruiting branches
Fruity branches appear from all nodes. Also, the difference between any branches of the plant is called the pot. Lastly, each fruity branches contain about 1~7 cotton as shown in Fig.

The growing of plants generally depends upon
- Fertility of soil
- Seed quality
- Climate conditions
The growth cycle of the cotton fibre plant
The cotton plant growth cycle generally can be divided into 5 stages.
- Germination
- Saddling
- Leaf area development
- Flowering and ball development
- Maturity of fibres
Germination and saddling
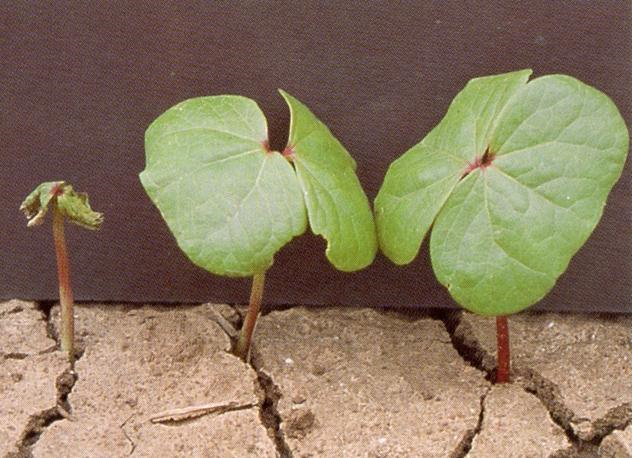

First of all small cotton plant grows from cotton seed. Afterwards growing of small plants take about 2~3 week and is called Seedling, as shown in Fig.
Leaf area development
During 20 to 80 days of development start the leafy area as the plant grows older.
Flowering and ball development
within 80 to 110 days creamy white colour flowers appear which later turn to pink at the end of the day. After the third day, the flowers whiter and hence dies to leave a small pod or tiny ball. Also, by the time the plant grows, the fibres continue to appear inside the ball.
Furthermore, cotton fibre developed on slight swelling of epidermal Layers of the seed inside the ball. Each swelling develops into a hollow tube and increases its length daily till it reaches its full length.
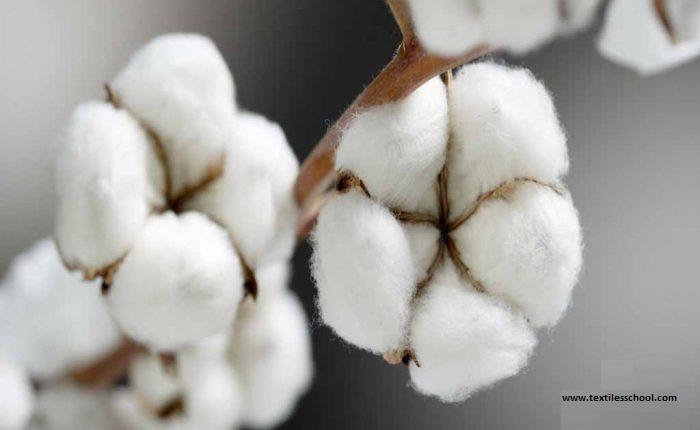

Up to the half growth cycle of fibre is completed and fibre is hollow in the form of only the primary wall. by the time the next stage of fibre development secondary layer of cellulose is added inside. The depositing of cellulose layers continues for several days in the form of reversing spirals. thus creating a structure similar in cross-section to the growth of the ring of the tree stem.
Maturity of cotton fibre
After reaching 55~80 days when balls reach maturity i.e. fibres and seeds tightly packed into the ball, the ball bursts and cotton fibres appear as soft and fine fibres.