What is air conditioning in textiles?
“Air conditioning is defined as the science dealing with simultaneous control of temperature, humidity, cleanliness, and distribution of air in enclosed spaces or in textile mills“.
Thus air conditioning involves
- Temperature control
- Humidity control
- Air filtering, cleaning, and purification
- Air movement and circulation.
The necessity of air conditioning in textiles
Air Conditioning in textile mills is a very important parameter in the working of textiles especially spinning and weaving; without an air conditioning system, the existence of these units is very difficult and impossible.
- Without air conditioning, some of the fibers could hardly be produced on a commercial scale or efficiently handed in different textile processes.
- Secondly, the production of cotton and other natural fibers is greatly affected by the use of proper air conditioning.
- The mechanical and electrical properties of natural fibers and yarn are greatly dependent upon environmental control.
- The moisture content and regain of hygroscopic materials in governed by humidity control and the number of waxes’ continued response to temperature.
- The reduction of static charges, air born Lint, dust, and thread breakage are the other advantages that directly contribute to greater productivity and better quality of fibers yarn, and fabrics
- Also, air conditioning provides a comforting healthy, and psychological effect on human beings
- Air conditioning thus enables the best result regarding properties, process, and production.
Factors to be considered by engineer before installing air conditioning plant
While installing the air conditioning plant, the following points are considered
- The estimation of load for winter as well as summer
- The heat generated by the running of machinery, lighting, process, and also the workmen should also be taken into consideration
- Well and badly fitted doors and the area occupied by windows are also kept in view.
- Solar and transmission losses and the roof load are also kept in mind
- The construction of the building and its age is also kept in mind
The complete air conditioning plant consists of

The complete air conditioning plant in textile mills involves
- Refrigeration plant or washer system.
- Heating coils
- Air cleaning and duct work
- Automatic control
Central station air washer system
The experience has shown that the refrigeration plant to required for a few days only in a year’s time and its high initial cost does not justify full air conditioning by refrigeration but the air washer system is, therefore, relied upon for giving the desired atmosphere in the sheds for all the year round. This is also known to be partial air conditioning.
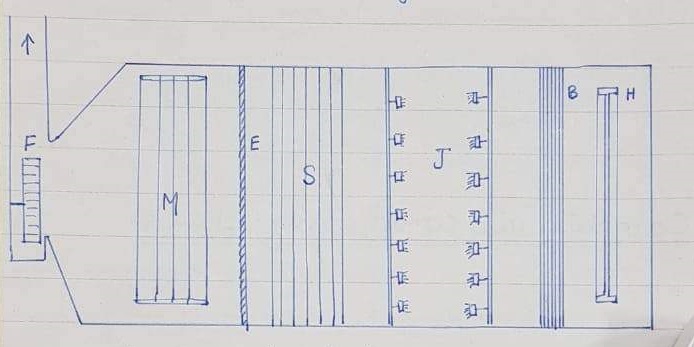
The sketch shows the central station air conditioning plant normally used in the textile industries for controlling temperature and humidity without the presence of a refrigeration unit.
In picture
H= tempering heater
B=baffle plate
J= jet in spraying chamber
S= scriber plates
E= elimination plates
M=main steam heater
F= fan
Working
The intake air which is a mix of fresh and returned air through the dampers is slightly heated at the tempering heater to prevent freezing in the water of cold entering air and also adjust the wet bulb temperature. A series of baffle plats (B) then follow to prevent the escape of spray and to provide correct air velocity uniformly across the whole area.
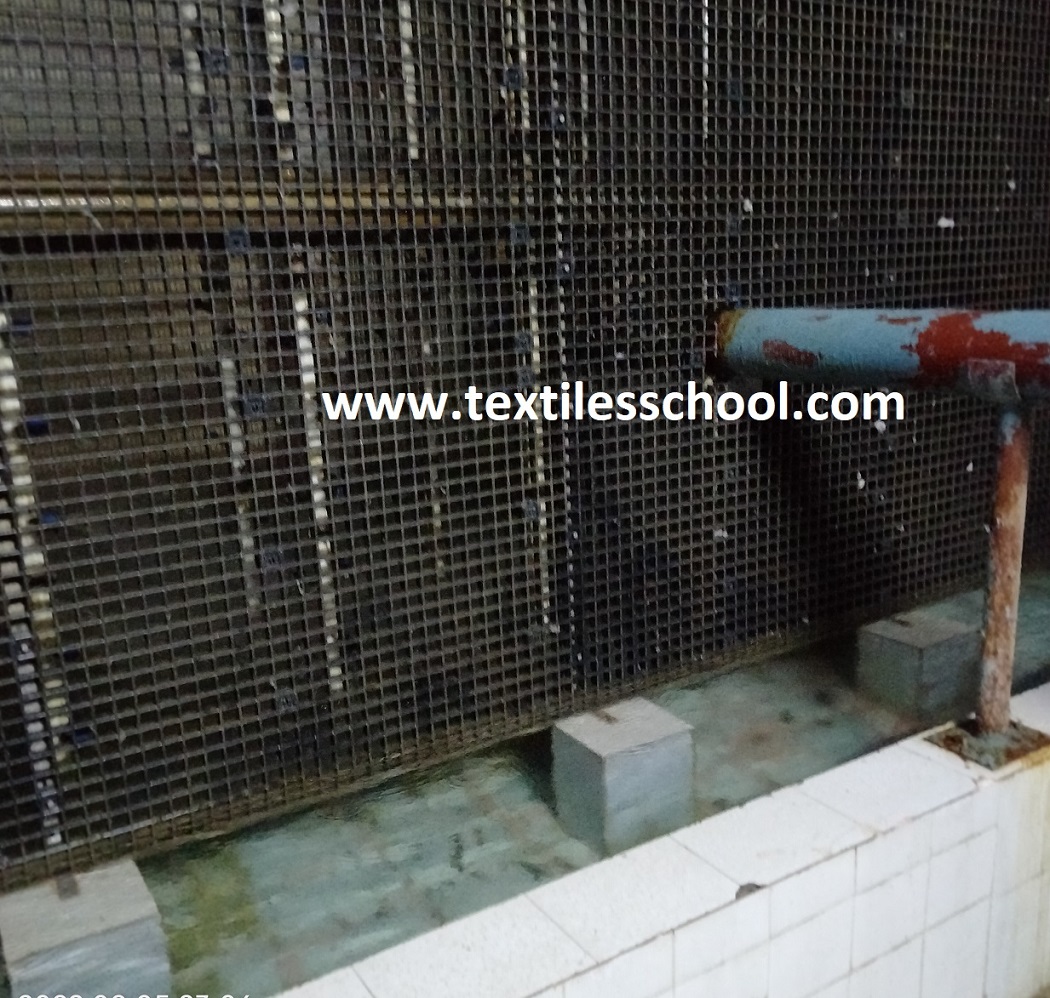

A series of parallel jets in opposite directions gives a dense spray chamber produced by pump pressure and jet action in the spray chamber. So the water from the sprays falls into the bottom tank from where it is reused by the pump after thoroughly cleaning it by passing through fine filters.
The air is drawn forward by the action of the fan and fine mist produced by jets is carried along. The complicated passage provided by the scrubber plates(S) washes down any solid matter by vertical jets. Also, a set of eliminator plates with projecting edges ensures the removal of all traces of suspended moisture and any other foreign matter.
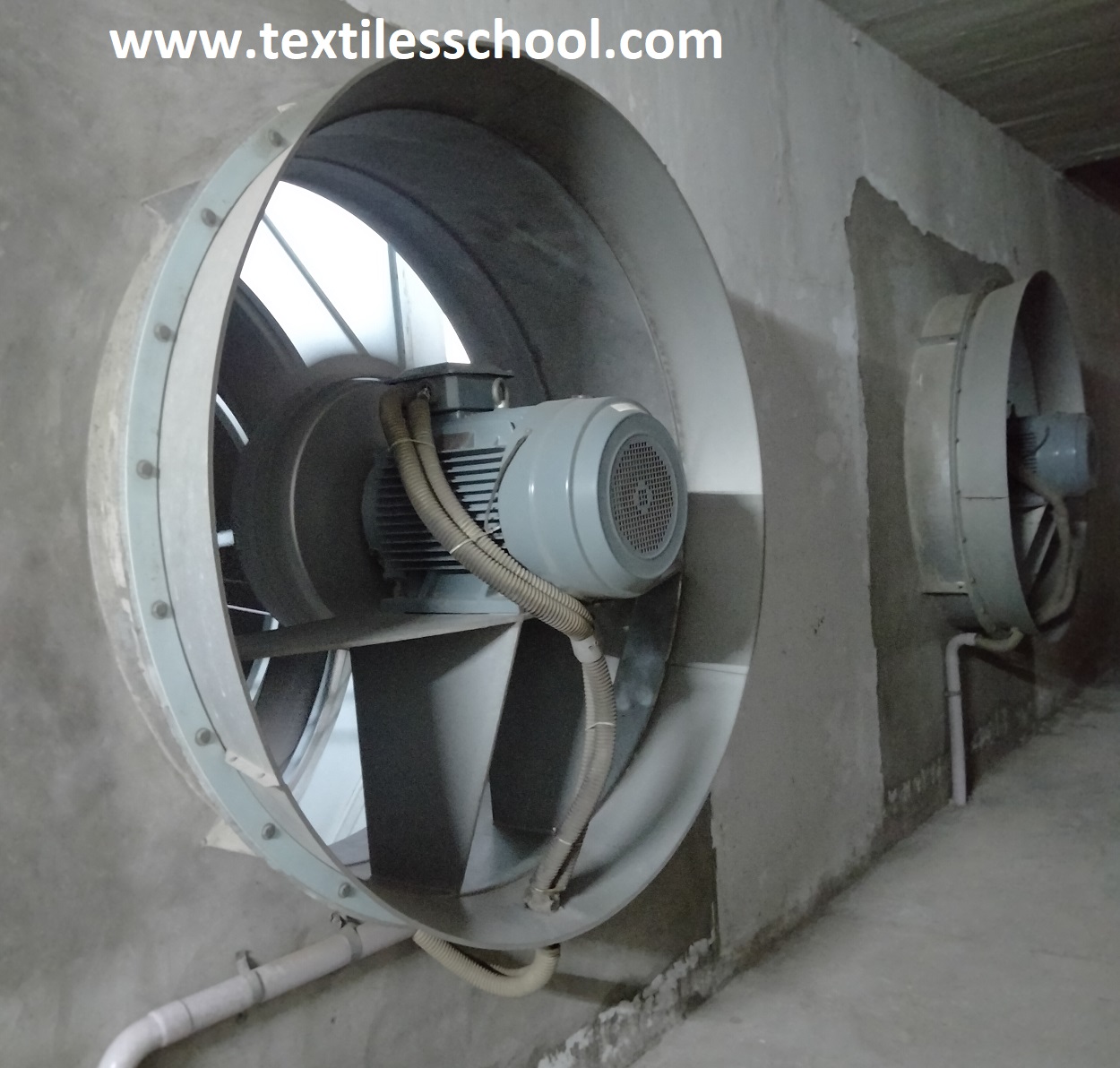

The fan circulates the air to the different departments which as stream coiled heater heats up the air to the requisite levels and separator control are inserted by thermostatic elements, so, when the cold water of tub-well is available for the sprays the air washes approaches the performance of refrigeration plant.
How air cleaning is done in an air conditioning plant
The open atmosphere, even in the country, contains a surprising amount of dust and grit. In the industrial areas, the amount of dust is increased with an appreciable amount of smoke, fog & other air and borne materials. In the case of the textile Industry, the trouble is further increased by lint & flies in the shed
The action of the air washer alone can not be relied upon for air purity & it must be assisted by some suitable air filters.
Air filters are of their types
1) Oil-coated impingement type (η20%)
2) Fabric type (η60%)
3) Electrostatic type (η90%)
The electrostatic type is the latest. Also, it arrests all particles down to 0.2 microns of tobacco smoke particles of 0.01 microns.
Automatic controls of air conditioning plant
The operation of air conditioning depends on the control system provided
The use of parchment strips to sense humidity by shrinkage of parchment & to open or close the water injection through operating levers is an old method but does not give as precise control.
Electronic controls are mostly used nowadays in which the impulse is made to operate a microswitch to adjust the water inlet valve.
The use of thermistors & other transducers has enabled electronic controls to be sensitive &reliable. The control of tamping of ± 10F and ±2% R.H is possible with these electronic control circuits.
What is relative humidity?
In simple, relative humidity (RH) is a measure of the vapor content of the water in the air. Also, more simply water moisture present in the air is considered in percentage as an (RH%). The relative humidity formula is
Relative humidity= ((Dry blub temperature – Wet blub temperature) x300/Dry blub temperature) -98.6
Here temperature is in degrees Fahrenheit.